ASME V Radiology Introduction
By Carlos Molina
This time we are going to check radiographic testing for welds in new tanks, an introduction. The BOK for the API 653 exam says:
2. Radiographic Examination:
The inspector should be familiar with and understand:
1. The Scope of Article 2 and general requirements [of ASME V].
2. The rules for radiography as typically applied on butt welded AST horizontal and vertical seams such as, but not limited to:
required marking type.
selection.
number, and placement of IQIs.
allowable density control of backscatter radiation
location markers
3. Records
I will try to simplify this subject as much as posible for the people who is studying for the API 653 exam.
SCOPE OF ARTICLE 2 AND GENERAL REQUIREMENTS
I don´t want to deal here with this issue, given that it is very broad and ideally should belong to another part of the BOK. Let´s first talk about procedures.
[adToAppearHere]
PROCEDURES
Any radiographic testing needs a written procedure approved by an level III supervising inspector, even whe the actual test can be done by a level II technician. This is like for any other NDE type, like Penetrant Testing, or Magnetic testing (API 650 Annex U). The procedure shall contain, as a mínimum:
- material type and thickness range
- isotope or maximum X-ray voltage used
- source-to-object distance
- distance from source side of object to film
- source size
- film brand and designation
- screens used
MATERIAL TYPES
There is not much to say here. Industrial radiography can be used in many industries, from concrete to medicine to ceramic aviation components, but mostly it is used for weld inspection. In our case we are talking of course, about carbon steel or stainless steel.
TYPES OF RADIATION FOR INDUSTRIAL RADIOGRAPHY
There are 2 main radiation sources used for industrial radiography.
X-RAY or GAMMA RADIATION
Radiation for industrial radiography is now usually distinguished by their origin: X-rays are emitted by definition by electrons outside the nucleus, while Gamma rays are emitted by the nucleus. X-ray can now be produced by electric means, using x-ray tubes, while gamma rays for industrial radiography will need a radionuclide., as cobalt-60 or oridium-192.
X-ray tubes
With isotopes, it is very difficult to achieve a small, compact beam of radiation aimed to your desired location, as you can do with X-ray tubes. Besides, isotopes can´t be turned off for the sake of safety. But X-ray equipment is heavier and requires a power source. The amount of radiation for X-rays depends on the voltage applied.
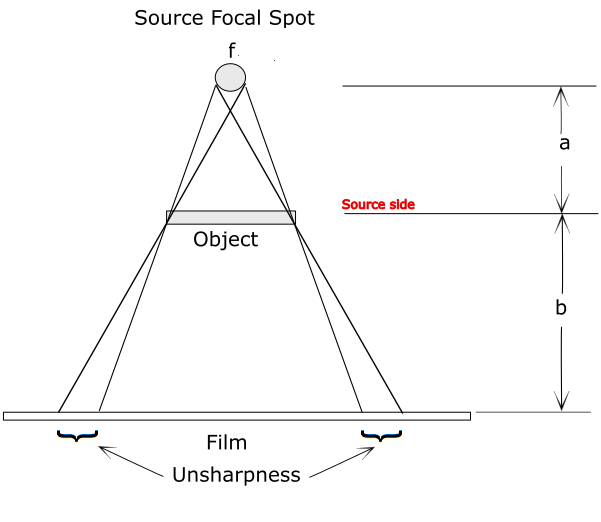
SOURCE-TO-OBJECT DISTANCE and DISTANCE FROM SOURCE SIDE OF OBJECT TO FILM
The ideal source-to-object distance and the distance from source side of object to film are given by a máximum value of geometric unsharpness present in most radiographies. Geometric unsharpness is the loss of definition, mostly of the edges, as a result of geometric factors of the radiographic equipment and setup. It occurs because the radiation does not originate from a single point but rather over an area.
Geometric unsharpness, Ug, can be calculated from the formula in the following image
SOURCE SIZE
Source size is important because a bigger source achieves a higher level of geometric unsharpness. For isotopes, source size is just given by a measure in mm or inches, of the diameter of the pellet or pellets used in the source capsule (pellets in the range of 1 or 2 milimeters are common). As for X-rays, several methods have been used to reduce the focal size of the X-rays used, depeding on the way the X-rays are created. Usually, reducing the angle of the catode in the X-ray tube reduces the source area.
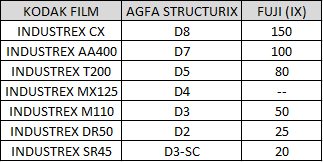
FILM BRAND AND DESIGNATION
RT Films Classification is like Class I,II etc or Type 1,2,3 etc. which is basically denoting the speed of film. Most popular brands for industrial radiography film are AGFA, Fuji and KODAK. There can be different types of films made by the same manufacturer within the same class. Take for example the DR50 and the M100 of Kodak, that are the same class but have different sensitivities. One of the most known films for radiography is the D7 of AGFA. Besides, the same film can have varying speeds depending on the source type. It takes an experienced person to select the right film for the application being. If you wish to review different designations for radiographic films, see te table below.
[adToAppearHere]
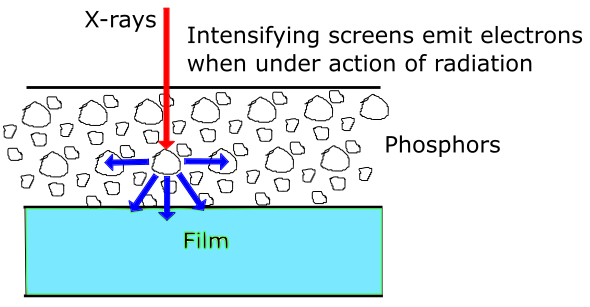
SCREENS USED
When we talk here about screens, we are talking about intensifying screens. Image in the radiographic film is the result of just 1 % of the amount of radiation energy created. The rest of the energy passes through the film and is not used. Sometimes this is not enough and intensifying screens must be used.
They can be made of several types of material (lead, steel, copper, salt, fluorescent materials, etc), and basically one front and one back screens are used to sandwich the film and make the image more clear. Fluorescent screens instantly emit light under the influence of electromagnetic radiation. The moment radiation stops, so does the lighting effect. Certain substances, as phosphors (usually rare earths) emit a lot of light when subjected to ionising radiation, and they have more effect on the light sensitive film than the direct ionising radiation itself, thus intensifying the image. A side effect of intensifying screens is, of course, a little more unsharpness.
SUMMARY
All of the numerals treated herein are to be included in the Procedure for Radiographic testing that needs to be signed by a level III. Next week we´ll see more information corresponding to radiology for the Body Of Knowledge.
Thank you and bye bye.
Latest comments
It is very useful to me.
- sakthivelValueable information,thanks a lots.
- Dennis TongI want this type of article
- sakthivelThis article very useful to me
- sakthivel